Raising Kidney Disease Awareness

More than 1 in 7 US adults have chronic kidney disease—about 30 million people.

More than 590,000 people in the US are living with kidney failure.
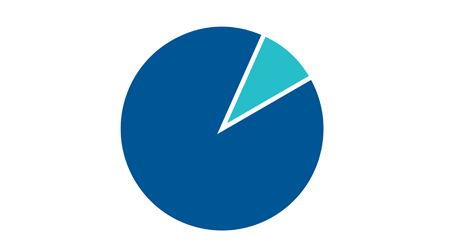
90% of people with stage 3 CKD don’t even know they have it.
Understanding CKD causes and risk factors
There are several health conditions that can cause kidney disease. Diabetes is the leading cause of CKD, followed by high blood pressure. Together, these conditions account for 73% of CKD diagnoses. Other causes of CKD include glomerular disease and polycystic kidney disease. If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, it is important to talk to your doctor about CKD and get screened. CKD symptoms for CKD are hard to detect, so testing is the most reliable indicator. The earlier CKD is detected, the sooner you can take the steps to slow progression.
Are you at risk? Know these risk factors
- Family history or age—family members with kidney disease or an age of 60 or older
- Health problems—a diagnosis of diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, obesity, or other kidney or immune conditions
- Ethnicity—African American, Hispanic, or Native American ethnicity, which may carry greater risk
- Lifestyle Habits—overuse of ibuprofen, acetaminophen or naproxen, or chronic use of street drugs
CKD testing and diagnosis
The earlier CKD is diagnosed, the sooner you can take steps to slow progression and delay the need for transplant or dialysis. Kidney disease is diagnosed with a simple blood test ordered by your doctor to determine your estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which is a measurement of how well your kidneys are functioning. You may also have other tests before a kidney disease diagnosis can be confirmed. Your eGFR determines which of the 5 stages of kidney disease you’re in and your doctor will make recommendations for taking care of your health, based on your stage.

Spread the word! Kidney disease awareness is important. About 15% of US adults have CKD, though many don’t realize it. Symptoms often don’t appear until late stages.
Ask your doctor about your kidney health.
Slowing progression of kidney disease
There are things you can do at every stage of CKD to help manage your kidney health and live your fullest life. In early stages, treatment goals may focus on managing other health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, as well as making healthy changes in diet and exercise. In late-stage CKD, your nephrologist (kidney doctor) may talk to you about a chronic kidney disease diet and considerations for kidney failure treatment. Planning ahead can give you more options should you need a transplant or dialysis.
Considering a kidney transplant
A kidney transplant is considered the best treatment for ESRD if you’re a good candidate. Kidney transplant is major surgery in which a person with kidney failure receives a healthy donor kidney to take over blood filtration and urine production. Candidates for kidney transplant must be in otherwise good health, have access to a good donor match and meet other health and timing requirements.
Dialysis: A lifesaving treatment
Dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that filters your blood to remove toxins, waste, and excess fluid using special equipment—taking the place of natural kidney function. There are several different options for dialysis—including peritoneal dialysis, home hemodialysis, and in-center hemodialysis. Your nephrologist can help you choose which option is right for you. Going on dialysis requires commitment to your treatment schedule, attention to eating well, and taking certain medications exactly as directed. When following their treatment plan as prescribed, people can live healthy, active, fulfilling lives on dialysis—and keep up with the lifestyle they love.

